Hein? 41+ Listes de Quadrants Labeled With Pi! Just go through above figure and it will be quite easy for you to understand the quadrants.
Quadrants Labeled With Pi | For now, just memorize the information. The rectangular coordinate system is divided into four quadrants labeled as quadrants i, ii, iii, iv b. Learn how to determine the quadrant of an angle given in radians. The angle is between the first and second quadrant. With ggplot2, can i add four quadrants. Graph quadrants labeled labeled quadrants labeled quadrants four quadrant graph paper. Recall that 1 radian is the distance on the circumference of the circle that is equivalent. To add pi labels to your x and y axes, click the graph settings wrench. For instance, in what quadrant does this lie: For now, just memorize the information. (and sorry for my bad english). Is in the second quadrant. For now, just memorize the information. For instance, in what quadrant does this lie: I wonder if this gives us any benefit, or if any historical/mathematical reasons behind it exist. When evaluating sine, cosine and tangent for the reference angle, determine if each value is positive or negative by identifying the quadrant the terminal side is in. Blank coordinate planes in 4 quadrant and 1 quadrant versions in printable pdf form. Basically just a line down the middle for the y and x axis (a plus sign)? 25pie/3 please explain your steps and reasoning. Learn how to determine the quadrant of an angle given in radians. At each angle, the coordinates are given. Recall that 1 radian is the distance on the circumference of the circle that is equivalent. The quadrant data series are two dummy series that will be used only to set the x and y axis for the quadrant dividers. If we go straight up, if we rotate it, essentially, if you want to think in degrees, if you rotate it counterclockwise 90 degrees, that is going to get us to pi over two. Just go through above figure and it will be quite easy for you to understand the quadrants. Learn how to sketch angles in terms of pi. You should use roman numerals to label your quadrants. I wonder if this gives us any benefit, or if any historical/mathematical reasons behind it exist. (and sorry for my bad english). Just remember the dividing axis lines so that it will be easy to specify the quadrants accordingly. Three pi over five, so we're gonna start rotating. I wonder if this gives us any benefit, or if any historical/mathematical reasons behind it exist. The quadrant data series are two dummy series that will be used only to set the x and y axis for the quadrant dividers. It lies between quadrants 1 and 2 as far as i can tell, the definition of the four quadrants does not include the axes. Learn how to determine the quadrant of an angle given in radians. At each angle, the coordinates are given. Wide collections of all kinds of labels pictures online. Quadrant 3 quadrant 4 quadrant 2 quadrant 1. How can i find exactly in which quadrant it lies? We can label the axes and add a title multiple lines can be shown on the same plot. For now, just memorize the information. It would be nice to also have the option to simplify fractions of pi or to write fractions of pi with a common denominator (such as pi/6 for the step). The point where the two axis intersect is called origin and is denoted. Angle is measured in radians or in degrees. 25pie/3 please explain your steps and reasoning. Each quadrant is equals to 90°. For instance, in what quadrant does this lie: When evaluating sine, cosine and tangent for the reference angle, determine if each value is positive or negative by identifying the quadrant the terminal side is in. So it lies between q1 and q2. Graph with the 4 quadrants labeled on a coordinate plane. Each quadrant is equals to 90°. • the cartesian plane is divided into 4 quadrants by the two coordinate axes. Pi/2 and pi is 2nd quadrant. You should use roman numerals to label your quadrants. Finally, to determine the quadrant, you just have to know that east is 0 pi, north is pi/2, west is pi, and south is. This value should be rounded toward zero to keep user computations with angles from inadvertently ending up in the wrong quadrant. Basically just a line down the middle for the y and x axis (a plus sign)? The labeling overlap is getting problematic. If we go straight up, if we rotate it, essentially, if you want to think in degrees, if you rotate it counterclockwise 90 degrees, that is going to get us to pi over two.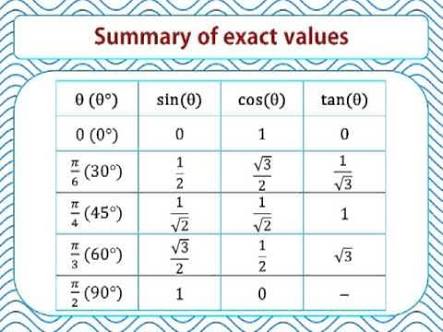
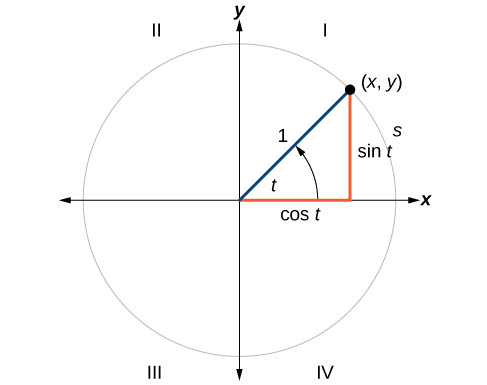

Each quadrant is equals to 90° quadrants labeled. Each quadrant is equals to 90°.
Quadrants Labeled With Pi: The point where the two axis intersect is called origin and is denoted.
Refference: Quadrants Labeled With Pi


0 Comment